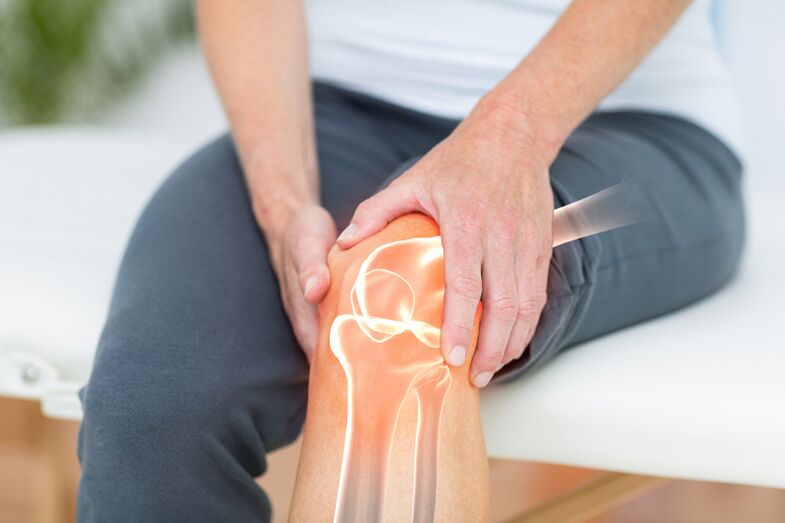
Causes of arthrosis
We can say that knee arthrosis is a disease, on the one hand, due to lifestyle, on the other hand, age.
The immediate (internal) causes of arthrosis are:
- past injuries in the joint area (sports, domestic and other),
- inflammatory diseases of the musculoskeletal system (arthritis),
- metabolic diseases (diabetes mellitus),
- common orthopedic defects of the lower extremities, including flat feet and valgus foot, X-shaped deformity of the feet; these defects affect the correct movements of the knee joints, leading to their deformation and degeneration of the articular tissues.
Factors (external, individual) that provoke arthrosis:
- overweight, overweight,
- female,
- age,
- constant heavy loads (work on the feet, monotonous movements of the joints with weights during the working day).
Under the influence of external and internal factors, degeneration and aging of the knee joint begins, all its structures are involved in the process: bones, cartilage, synovial membrane, joint capsule, ligaments.
Symptoms of arthrosis
Manifestations from the knee joints are directly related to the stage of arthrosis. The more pathological changes in the joint and adjacent tissues, the more pronounced the symptoms.
- In the initial stages, a person may be bothered by discomfort, mild pain after physical activity, passing on its own.
- Over time (from 1 year to several years), the pain intensifies, becomes permanent, joint movements are limited, a characteristic "crack", "crack" appears when moving.
- In the final stage of gonarthrosis, movements are severely limited, the joint is visually deformed, walking is difficult and severe complications can develop up to complete immobility ("joint mice", joint fusion, etc. ).
Diagnosis of arthrosis of the knee joints
Arthrosis of the knee joint is detected using available diagnostic methods:
- Ultrasound of the knee joint allows you to assess the condition of the cartilage and bone surface of the joint, the surrounding soft tissues; is of particular importance in the initial stages of arthrosis, as it helps to identify pathological changes even before the appearance of serious symptoms;
- radiography is also one of the main diagnostic methods, but it is not always available, in addition, it is associated with exposure to radiation in the body;
- MRI, CT and arthroscopy are also used to clarify the diagnosis or to identify the features of the course of the disease.
Treatment of gonarthrosis
In arthrosis of the knee joint, different exposure methods are used:
- drug therapy, including intra-articular administration of drugs,
- traction (discharge) therapy,
- physiotherapy, classic and innovative methods,
- physiotherapy and massage,
- manual therapy,
- autoplasma therapy (PRP-therapy).
The combination of these methods, chosen by the doctor, can reduce the symptoms of arthrosis, stop inflammation and degeneration of the joint, preserve its mobility and range of motion.
Initial stages of arthrosis
In the initial stages of the disease, drugs with an analgesic and restorative effect (NSAIDs, chondroprotectors, vitamins) are used, they are prescribed by a doctor. In addition, a variety of orthopedic tools are used: insoles, shoe inserts, special shoes). Physiotherapy, manual massage, physiotherapy exercises give a good effect.
A visible effect of the treatment does not occur immediately, but if the doctor's recommendations are followed, the condition improves.
Progressive arthrosis
More serious measures are required here, in these cases the doctor can use minimally invasive interventions - arthroscopy, introduction of enriched plasma into the joint (PRP therapy).
In severe forms of arthrosis, severe pain, with accompanying synovitis (accumulation of excessive intra-articular fluid), corticosteroids are injected into the joint, which leads to rapid pain relief. The method is considered one of the most effective and, if the intervention is carried out correctly, there are no complications (rarely it is possible to increase the pain as a reaction to the drug, a negative effect on the cartilage and some others).
Among the surgical methods that maintain the functionality and range of motion in the joints, arthroplasty, arthroscopy and endoprosthetic operations deserve attention.
Treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee in a professional clinic
In a professional, modern clinic, experienced surgeons and arthrologists conduct appointments. The clinic uses an individual approach to each patient, performs accurate diagnostics using expert-class equipment (ultrasound), selects the optimal combination of treatment methods, taking into account the stage of arthrosis and the main symptoms, and prescribes timely medications to reducepainful manifestations.
Knee arthrosis is rightly considered an age-related disease, but its development can be prevented or slowed down if the condition of the joints is assessed in time and therapy is carried out (for preventive or therapeutic purposes).
The professional clinic offers physiotherapy procedures (electrophoresis, darsonval, massage, acupuncture) and minimally invasive interventions (arthroscopy, intra-articular injections) that improve the condition of the joints, supportive courses of medication are prescribed to help consolidate and prolong the effect of the joints. main therapy, to prevent deterioration.